|
We, the Board of Directors and the Team at KISMC, are extremely sad to announce to all club members, partners, friends and supporters that Marionela Simova is no longer among us. Following a brief period of illness she sadly left us. Marionela was a co-founder, project manager and a well-respected colleague at KISMC.
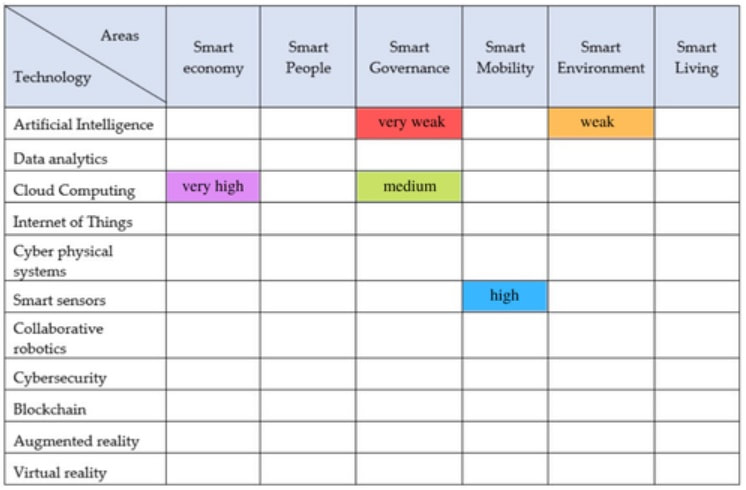
Marionela played a crucial part in the set up of the club back in 2012. She was extremely dedicated and with a very high level of professionalism she helped to get it off the ground successfully. She enthusiastically supported the foundations of KISMC and participated actively in the management of all projects - some have already been successfully completed, others are still in implementation. Marionela strongly believed in the mission of our organization and had always dedicated her time and experience voluntarily to achieve the goals of the club. She will stay in our hearts forever! The SMART project is aimed at developing new competencies of the SMEs managers to manage deep-tech businesses in one very fast-growing market - the smart cities. The penetration of so-called smart city technologies results in the creation of new markets and requirements for new skills. On the basis for the achievement of this purpose is laid the map of digital smart disruptions. This short article explains some important terms and the approach implemented in this project. What is a Map of Digital and Smart Disruptions (in the context of smart cities)?The picture is worth a thousand words - Fred R. Barnard. The map of digital and smart disruptions provides an easy for understanding and learning overview and analysis of how digital and disruptive technologies (innovations) do shape the smart city concept. The map includes the results generated by the focus group and corrected later by the partners with the results from the research on the technologies advances, level of change and impact, performance, purpose, and fit. The map is a two-dimensional cross factorial analysis matrix made with different instruments in diverse forms (Fig.1). Fig.1. Mapping the disruptive smart city technologies (the filled areas are only exemplary) The ultimate purpose of a map is to improve the scenario planning of businesses and the cities in the process of their transformation into smart cities and to point out the opportunities for involvement of the businesses in the process. So, this can be treated as a sample of an opportunity map for every city in the process of urban management and for every company in the process of innovation management. In the case of the project SMART, the map will present the results of the studies and research of the project partners in a systematic and simplified way, based on:
What is a Disruptive Smart City Technology?The definition of the disruptive innovation given by Clayton Christensen is the innovation that creates a new market and value network and eventually disrupts an existing market and value network, displacing established market-leading firms, products, and alliances. The following benefits and changes coming from the disruptive innovations are identified:
Following this definition, it is easy to presume that in general the “disruptive smart city technology” is any kind of emerging, advanced & digital (but not only) technology that can generate disruptive innovations creating benefits and many changes in the context of an urban (territorial) area and if this process is well managed it should result in a better life of the citizen. What Does the Process of Mapping the Smart City Disruption Mean? The mapping is a structured process, focused on a topic or construct of interest, involving input from many participants, that produces an interpretable pictorial view (concept map) of their ideas and concepts and how these are interrelated. The mapping helps partners to think more effectively as a group without losing their individuality. It helps the project group to manage the complexity of the vision on the smart city disruptive technologies without trivializing them or losing detail. The mapping process is one of the portfolios of many other similar methods that management and social scientists have developed like brainstorming, brainwriting, nominal group techniques, focus groups, affinity mapping, Delphi techniques, facet theory, and qualitative text analysis. The mapping process is focused on the major shifts from the business perspective and how these changes will affect the growth. It uses focus groups to understand and analyse the impact of smart city technologies and their application for business growth. The trends, types of technology, and levels of transformation are included in studying within the process. Consequently, the project partners have to study a framework of the following five dimensions of these technologies:
The study includes the level of impact and change of the emerging technologies - so, what does exist now and what is the current maturity level (according to Gartner). What Stages Does the Process of Mapping Include in a Focus Group? The process is placed in a focus group that is facilitated by the leader of the mapping process. A mapping process in a such group involves five steps that can take place in a period of time, planned for the output and depending on the project development situation.
The Article was first published on the Smart by Design website, blog content. This article is animated by the interim results of an ongoing Erasmus+ project named Smart technologies by design (Smart by Design). The project is being carried out by the following partners:
In a number of articles the project partners of Smart by Design present their findings and deliverables generated and developed during the project execution. Our attention is focused on the gap between the citizen's (smart cities') needs, the technological solutions which can cover these needs, and the knowledge and skills of citizens, cities and service providers of using these technologies for a better life. Technologies Make Cities SmarterDisruptive technologies have the potential to transform the way cities currently operate and they are at the core of nearly all upcoming smart city’s solutions. After a decade of experimentation, smart cities are entering a new phase. Although digital solutions are only one of the tools needed to make a city great, they are the most powerful and cost-effective additions seen in many years. According to the McKinsey Global Institute, digital solutions could improve some quality-of-life indicators by as much as 30 per cent. Real-time crime mapping, for instance, utilizes statistical analysis to highlight patterns, while predictive policing goes a step further, anticipating crime to head off incidents before they occur. Another example of these solutions is the Internet of Things sensors on existing infrastructure systems which can help crews fix problems before they turn into breakdowns and delays. If we examine our history, we realize that we live in constant change. Humans have faced all sorts of changes, economic, political, climatic, technological. In the different industrial revolutions seized, adaptations made by humans can be perceived, along with the 1st industrial revolution, the railway arrived with the steam engines which enabled transportation of goods causing all the farming, demographic and transport revolution. Afterwards, the 2nd industrial revolution arrived, emerging new energy sources like oil and electricity, which with its utilization, first technological innovations took place. These technological innovations produced an improvement in the quality of life of people, first personal computers and the internet appeared which located us before a 3rd industrial revolution, not only in a technological one but in a scientific and a cultural one. With this 3rd revolution, fast technological advances force humans to assimilate more concepts in a shorter time, information, productivity and everything reach scales not previously reached and under this context the 4th industrial revolution appeared, where we really perceived and realized that we live in a constant change, as mentioned at the beginning, achieving small or big progress which is changing the world. A Vision of the Cities of the FutureThe city of the future must meet the needs of its residents. Yet in surveying residents of 25 major cities, McKinsey found out that a fifth of those cities fall short of delivering satisfaction. Respondents cited numerous inadequacies: crime, congestion, fire emergency response, waste management, active mobility options, police security, lack of basic utilities, public transit, as well as poor quality of housing and government services. Given the fierce competition for talent across cities, dissatisfied urbanites are likely to vote with their feet and leave for more attractive environments. (Source: Thriving amid turbulence: Imagining the cities of the future; Capital Projects & Infrastructure, Public Sector October 2018, McKinsey & Company). In order to not lag behind due to inactivity, the city leaders must know how to use the newest and most advanced technologies, which are progressing faster than expected. As a result of the study and during the implementation of the project we have realized that the most important and those with enough predictive potential to transform the cities into smart cities are the following technologies (technology areas):
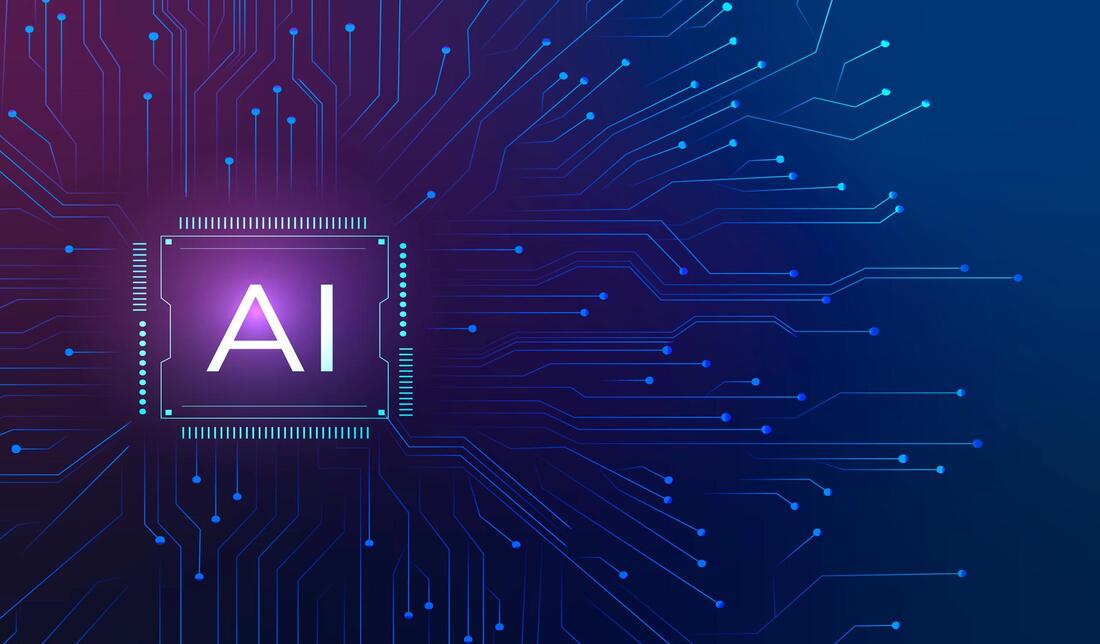
Artificial IntelligenceWe start with the first area - Artificial Intelligence (AI) and below you can find the features, functionalities, existing platforms, and standards, which are recognized by us as the most important from the point of view of upcoming evolving and disruptive solutions in the smart cities. Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the technology which aims to create intelligent machines that react and work like humans. Some of the skills for the computers with AI are the speech recognition, learning (information acquisition and patterns to use it), reasoning (using rules to reach definitive conclusions), self-correction and problems solving. This technology allows machines to learn from past experiences, adjust to new inputs and perform tasks like humans. Nowadays, the AI refers to a big range of concepts, from robotic process automation to the current more sophisticated robots. It has evolved due to the huge amount of available data or the increase of speed, size and variety of data that companies are collecting. The AI is also able to realize tasks such as the identification of patterns in data in a much more efficient way than humans, which allows companies to extract better conclusions from the information. Artificial Intelligence can be categorized in different ways and types of activities that they perform . But basically, the tasks that a computer based on AI can carry out, can go from developed very concrete tasks (faint AI) to other systems provided with human cognitive skills (strong AI), being able to give answers to problems or tasks that previously were not assigned or expected to them. In recent years, AI has grown capabilities thanks to the advance of some technologies, such as:
Existing PlatformsPlatforms for AI are hardware architectures or software frameworks that allow the software to run. Even if there are many different types of platforms related to this technology, some of the most relevant are: Published StandardsThe European Commission has launched the Communication COM (2018) Artificial Intelligence for Europe which establishes a new initiative for Europe about AI. This recognizes the need of the standardization as an answer to the challenges of this key technology, especially in terms of security, trust and ethical considerations. CEN and CENELEC support the fulfillment of the European legislation with harmonized standards. In relation to international organizations, the ISO has a technical committee which is working on the development of standards in Artificial Intelligence, which is the ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 42. There are currently two published ISO standards under this working group, and there are some more which are being developed. Published standards:
Application AreasArtificial Intelligence is a term which has existed for many years, but due to the development that current technologies are having, it has been recently spread to different application sectors and environments. Some of them are:
Expected Development Over TimeAs one of the main technologies which will help to evolve our ways to work and interact with technology, the trend is that the AI will keep growing and becoming more normalized in our society. So, platforms, standards, and applications will keep incrementing. PlatformsApparently, the future of the AI resides on a deeper personalization, innovation in voice AI and a better view of the customer. Even if there are plenty of platforms for AI, not many of them are deploying voice interfaces. Some applications for mobile devices have already implemented it in daily life and it will offer opportunities for companies. The tendency will be to add voice control to their AI for a better experience with their customers. Some of the most famous firms (Google, Amazon...) are integrating voice assistants as part of their services. The AI will help for a bigger personalization of services. Customers will be able to express preferences to the biggest brands and acquire much more personalized services or products. So, future platforms will shift towards a new type of services. Upcoming StandardsThe European Commission foresees that Artificial Intelligence will impact the commitment of some European guidelines. It will have effects in several sectors in which standardization is very relevant: smart manufacturing, robotics, autonomous driving, virtual reality, health sector, visual recognition, data analysis and management, domestic tools or cybersecurity. In all those sectors there are already essential standards which will need to be updated in order to add this new technology. Currently, there are four standards under development from the working group ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 42:
Potential ApplicationsEven if Artificial Intelligence is becoming more common in our daily life, there are many more applications foreseen or improved such as:
Sources:
The Article was first published on the Smart by Design website, blog content. This strange but memorable pandemic year is coming to an end. Like any organization that has set clear goals and priorities, the Knowledge, Innovation and Strategies Management Club (KISMC) reports to its members with another successful year. At the National Valorization Conference that took place in Sofiа on 18.12.2020, KISMC was awarded a certificate of quality for the successful implementation of the project Boost Aid for Social Entrepreneurship through Training (BASET). Such awards were given to only 40 projects out of 1500 projects in total from different categories, and this project is the only one to receive the award in the field Adult Education. Since the very end of 2019 and in 2020, we've launched seven new projects under the Erasmus+ programme, remaining loyal to one of the most successful human resources development under EU programmes. Namely, these projects are:
In such a way for the last few years since its establishment, KISMC has joined as a partner or leading organization 15 projects in total under the Erasmus+ Programme, 6 of which are finalized successfully and 9 are undergoing. By joining these projects, we remain fully committed to the topics that we consider very important for the development of our country, namely knowledge, innovation and entrepreneurship and, of course, the impact of new technologies and methods in these areas. Being also an active member of the Cluster Sofia Knowledge City, our organization KISMC supports with a part of its HR capacity three quite interesting and important projects that the cluster is realizing currently as a member of international partnerships, namely:
As a result, KISMC expanded its international presence in cooperation with over 20 new organizations from Europe, enriched its knowledge and experience in the field of knowledge management and innovation in SMEs, and developed and disseminated new useful methodologies, tools and good practices in these areas for the benefit of the Bulgarian business and the non-governmental sector. Internet of Things (IoT) is a term for physical devices connected to the internet which can collect and share data. Those devices can also include objects that have sensors allowing them to communicate in real time. Some examples: smart speakers, thermostats, lightbulbs, cars, fitness trackers, etc.
According to the Center for Internet Security (CIS) the IoT devices should have a connection to transmit the data as well as be uniquely identifiable, usually done through an IP address. There are multiple methods of communicating and transmitting data such as bluetooth connection, internet cloud-based service, wi-fi, etc. Nowadays, IoT devices are part of our daily lifestyles. It is estimated that by 2025, there will be over 20 billion IoT devices around the globe. Moreover, IoT is considered one of the 12 most important technological trends of the future. The benefits of IoT are evident, however, we keep seeing high-profile attacks occurring which creates an additional barrier for many businesses to adopt this technology. A research on the consumer attitude towards Internet of Things in Australia, Canada, France, Japan, UK and US revealed that 63% of consumers find connected devices "creepy". According to EDUCBA the 5 top benefits of internet of things for businesses are:
IoT is booming so is the number of attacks and security threats. It's immensely important to consider user safety and data confidentiality. The Knowledge, Innovation and Strategies Management Club, as part of the EU project - Internet of Things Security Nuggets (IoT Nuggets), co-funded by the European Union. along with its project partners from Bulgaria, Greece, Spain and Italy are developing a new methodology and framework with a model of digital competence for the Security of the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem including security and privacy to face the challenges that cybersecurity put in place. It is targeting VET providers and trainers in the ICT field, software engineers and programmers who want and need to update their competences, skills, and knowledge in cyber security of the ecosystem of IoT. And, ICT entrepreneurs who have, want, and/or would like to start a business in the IoT field. According to Deloitte in their document "Preparing tomorrow’s workforce for the Fourth Industrial Revolution For business: A framework for action" many employers are currently struggling to find talent due to the mismatch between skills and employers' needs. Technology has changed the way we work and live, and how businesses are operating. Automation and digitization greatly impact the skills required for specific jobs. But unfortunately a great number of organisations are not prepared for the transition to Industry 4.0, especially in terms of their workforce. This transformation in the new digital era brings in the creation of new jobs, but also the loss of many. Physically demanding, manual or routine jobs will decrease, and those that require problem-solving, flexible responses and customization will increase. In order to support this transition businesses will need to upskill and reskill their employees, and implement a culture of continous learning. L.E.K Consulting's manufacturing survey revealed that automation is motivating decision-makers in manufacturing industries to actively invest in their workforce and four out of five say that they are preparing for an increase in automation technology. In their blog article 'The Smart Way to Prepare Your Workforce for Industry 4.0' L.E.K also suggests following the three Rs approach to preparing workforce of businesses for the transition to Industry 4.0:
The TransIT project, co-funded by the Erasmus+ programme of the European Union, that the Knowledge, Innovation and Strategies Management Club is part of, is developing an innovative curricula, educational methods and training courses that guarantee an effective transition to Industry 4.0 standards. The project will provide a solution for company leaders, industry executives, HR professionals, SMEs and VET centers.
The TransIT project is producing three main elements that together will form a complete training kit, whereas each element will offer strong capacity building and help to successfully adjust to the forthcoming challenges of Industry 4.0 standards regarding the future of work. As part of the Training Kit we are preparing under the TransIT project, we synthesise good management practice enabling the transition to Industry 4.0 with three main overarching topics: innovation thinking, motivation management and technical cooperation. It also consists of the most relevant concepts relating to adaptive management. For more information on this kit - guidebook, read here. According to McKinsey, the new wave of automation and digitization brings its set of challenges, especially a great impact on the skills of the workforce. The new automation revolution will enormously affect employment and most organisations are not prepared to address the needs of their workforce to meet the needs of Industry 4.0. Hence, the TransIT project, co-funded by the Erasmus+ programme of the European Union, that the Knowledge, Innovation and Strategies Management Club is part of, is developing an innovative curricula, educational methods and training courses that guarantee an effective transition to Industry 4.0 standards. The project will provide a solution for company leaders, industry executives, HR professionals, SMEs and VET centers. Partners in the project are: Trebag (Hungary), NUI Galway (Ireland), Chamber of Commerce and Industry of Slovenia - Institute for Business Education, Weople (Portugal), KISMC (Bulgaria), IDEC (Greece), ARTO (Hungary), Robot-X (Hungary). The TransIT project will produce three main elements that together will form a complete training kit, whereas each element will offer strong capacity building and help to successful adjust to the forthcoming challenges of Industry 4.0 standards regarding the future of work. The future of work will require two types of changes:
Highlights from the McKinsey blog article "Building the vital skills for the future of work in operations"
Overall, companies have a number of approaches to address the skills gap created by Industry 4.0:
The fourth Industrial Revolution (Industry 4.0) is the ongoing automation of traditional manufacturing and industrial practices, using modern smart technology. It is the altering of the way products are created by spreading digitized manufacturing/processing and automation. The goal of Industry 4.0 is to increase the amount of usable data and improve decision making. Nowadays many organisations still don't understand how Industry 4.0 could impact their business as well as are struggling to find the know-how or workforce to support their transition. The Knowledge, Innovation and Strategies Management Club is part of the TransIT project, co-funded by the Erasmus+ programme of the European Union. We are aiming to develop and provide innovative curricula, educational methods and training courses that guarantee an effective transition to Industry 4.0 standards. Moreover, the project is developing work-based competences necessary for managing the transition to Industry 4.0. Read more about the TransIT project's objectives here. The project will provide a solution for company leaders, industry executives, HR professionals, SMEs and VET centers. We strive to inspire these groups to innovate and optimise their potential in the times of transitioning to Industry 4.0. According to Worximity, more and more technologies will be implanted in factories, there will be increase in the human-machine interactions and new jobs will be created, whilst employers will look for a variety of skills related to the transition to 4.0.
In one of their blog articles, Worximity suggests a number of tips to address the changes impacting the workforce in the era of Industry 4.0.
Cyber security is crucial for preventing harm to the integrity of the electronic devices and services that individuals and businesses use daily, as well as ensuring the confidentiality of the data stored and transmitted.
Cyber security involves the use of processes, technologies and controls for the protection of devices, systems, networks and data from cyber attacks and the ability to recover from these attacks. According to CENSIS the difference between IoT cyber security and IT cyber security is that IoT devices are connected to the physical world. The environments that IoT devices operate in are more diverse than traditional IT systems. Those who commit IoT cyber attacks range from hackers who work alone, small criminal groups, nation states involved in wider espionage, etc. Overall, awareness of IoT security is growing quickly. Kudelski reveal that management has begun to understand that in order to create a sustainable and competitive connected business security plays a key strategic role. Hence, Knowledge, Innovation and Strategies Management Club, as part of the EU project - Internet of Things Security Nuggets (IoT Nuggets), co-funded by the European Union, together with its project partners from Bulgaria, Greece, Spain and Italy, is developing a new methodology and framework with a model of digital competence for the Security of the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem including security and privacy to face the challenges that cybersecurity put in place. The IoT Nuggets project is targeting VET providers and trainers in the ICT field, software engineers and programmers who want and need to update their competences, skills, and knowledge in cyber security of the ecosystem of IoT. And, ICT entrepreneurs who have, want, and/or would like to start a business in the IoT field. To find out more about the project, read here. The TransIT project, co-funded by the Erasmus+ programme of the European Union, develops and provides innovative curricula, educational methods and training courses that guarantee an effective transition to Industry 4.0 standards. The project will provide a solution for company leaders, industry executives, HR professionals, SMEs and VET centers. Partners in the project are: Trebag (Hungary), NUI Galway (Ireland), Chamber of Commerce and Industry of Slovenia - Institute for Business Education, Weople (Portugal), KISMC (Bulgaria), IDEC (Greece), ARTO (Hungary), Robot-X (Hungary). Below you can find more information on the project and how it enhances innovation and motivation in the workforce towards the transition to Industry 4.0: For additional information about the TransIT project, read here. |
KISMC TeamBlog post by our team, innovation contributors, VIP members, blog guests, etc. Archives
January 2024
Categories
All
|
|
The Knowledge, Innovation and Strategies Management Club is a non-profit organisation set up in Sofia, Bulgaria in 2012 to foster knowledge and innovation management across South East Europe. KISMC is supporting the development of the innovation ecosystem in the region by bridging the gap between education, research and business.
|
© COPYRIGHT 2013- 2021. KISMC. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
|












 RSS Feed
RSS Feed